
Inventory Management System (IMS)
Introduction
Managing complex inventories of high-value components is a challenge faced by many scientific and industrial facilities. The Inventory Management System (IMS) is a web-based platform designed to streamline the tracking, organisation, and lifecycle management of thousands of items such as optics, electronics, and mechanical parts.
The Problem
Scientific and industrial facilities use complex systems such as vacuum chambers, detectors, lasers, and specialised equipment, where downtime is costly and disruptive. Traditional inventory tracking methods like spreadsheets and static documents cannot keep pace with growing operational complexity. As facilities expand, a centralised, dynamic, and intelligent inventory solution becomes essential to maintain efficiency and minimise downtime.
Facilities often struggle with:
Limited visibility — Unclear what parts exist, where they are, and their condition.
Fragmented catalogues — Data scattered across spreadsheets and local documentation.
Inefficient spare-part management — Leads to shortages, overstocking, and delayed maintenance.
Lack of predictive insights — No forecasting for part lifetimes or replacement needs.
Our Solution
IMS provides a web-based system to store, track, move, and itemise your inventory. Categorise different parts, create individual records for physical entities. Move them between systems, tracking their usage status. IMS keeps track of spares, so you will always know when the best time to order new parts is.
IMS provides:
A centralised, browsable catalogue of all components used in the facility.
Real-time tracking of all physical parts as they move through storage, operation, and scrap.
Automated spare-part calculations based on current stock, location, and usage conditions.
Predictive spare insights that estimate when new parts should be ordered based on expected lifetime, time to replace, items in use, and current spare counts*.
Predictive part lifetime insights that estimate part lifetimes by analysing historical usage and failure data*.
Below is an example use case of IMS for a Scientific Research Facility:
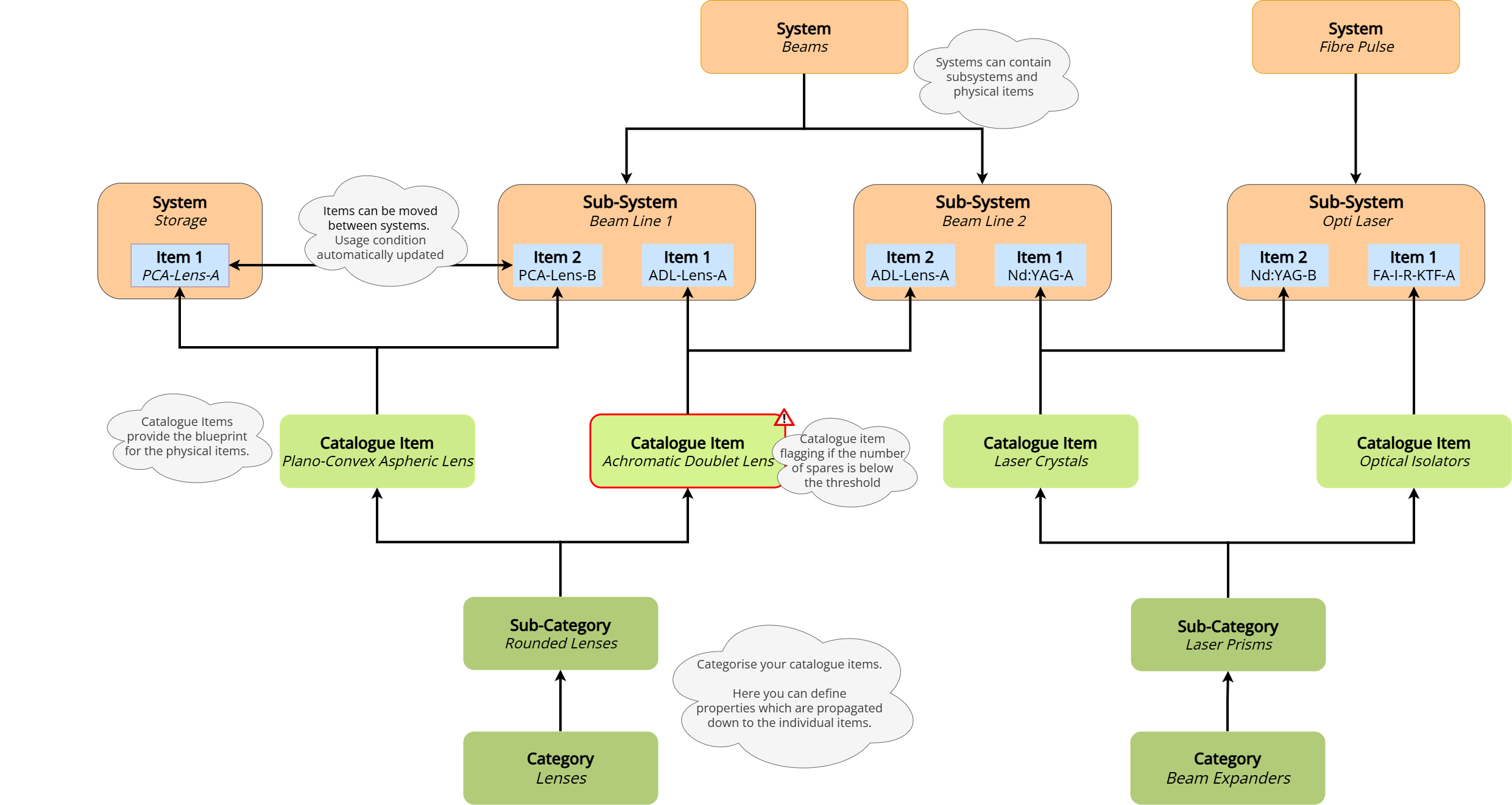 IMS structure overview: Detailed categorisation, for catalogue items and systems. Items which can move dynamically between systems. Our solution provides a comprhensive overview of your inventory.
IMS structure overview: Detailed categorisation, for catalogue items and systems. Items which can move dynamically between systems. Our solution provides a comprhensive overview of your inventory.Quick Glance
Below are several key interfaces that highlight the functionality and design of the system:
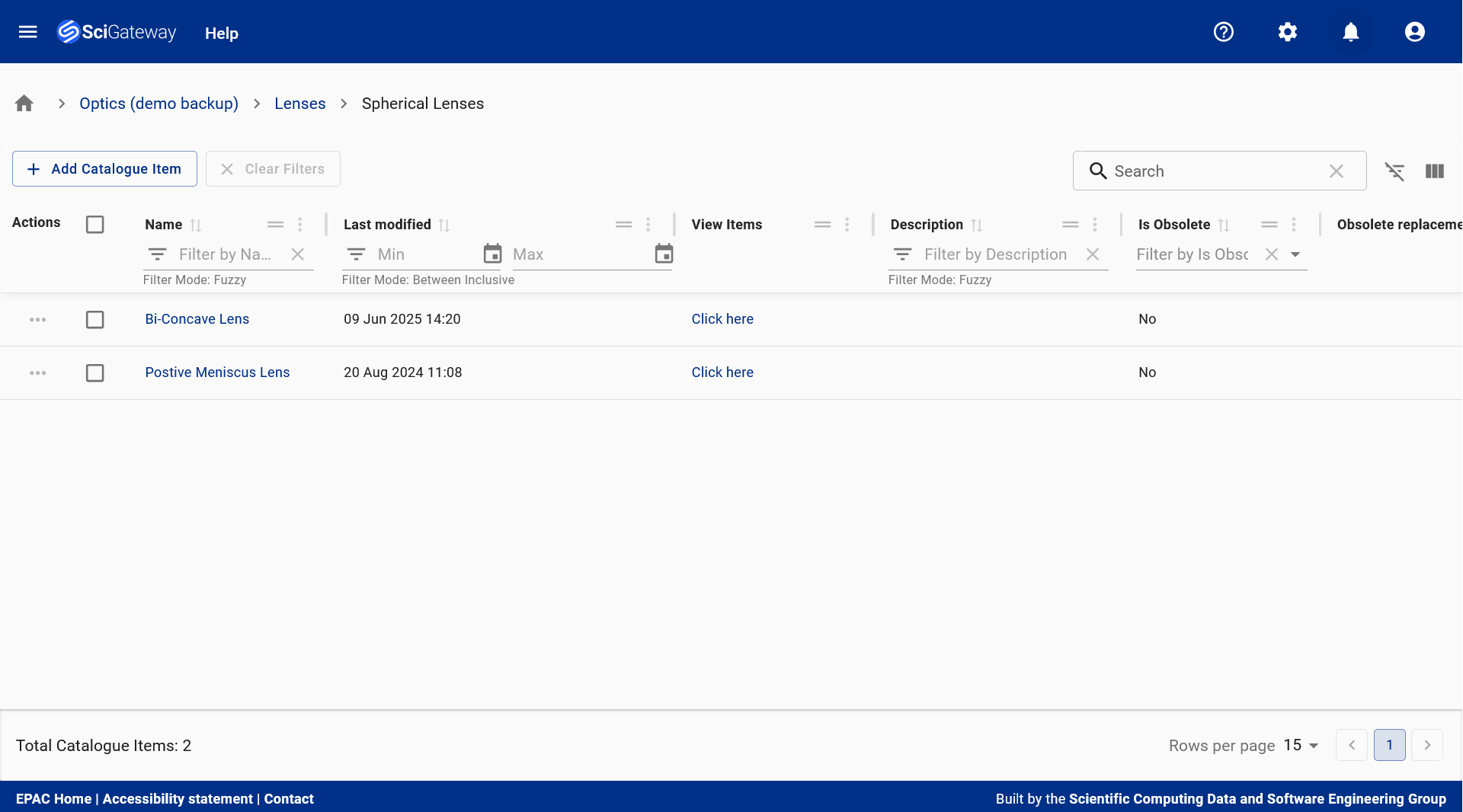 Catalogue Items Table: Displays structured commercial representations of physical items, including names, descriptions, lifecycle status, and procurement details - supporting efficient planning, quoting, and inventory management. Here you can also view the number of spare items, a key indicator for when to purchase more inventory.
Catalogue Items Table: Displays structured commercial representations of physical items, including names, descriptions, lifecycle status, and procurement details - supporting efficient planning, quoting, and inventory management. Here you can also view the number of spare items, a key indicator for when to purchase more inventory.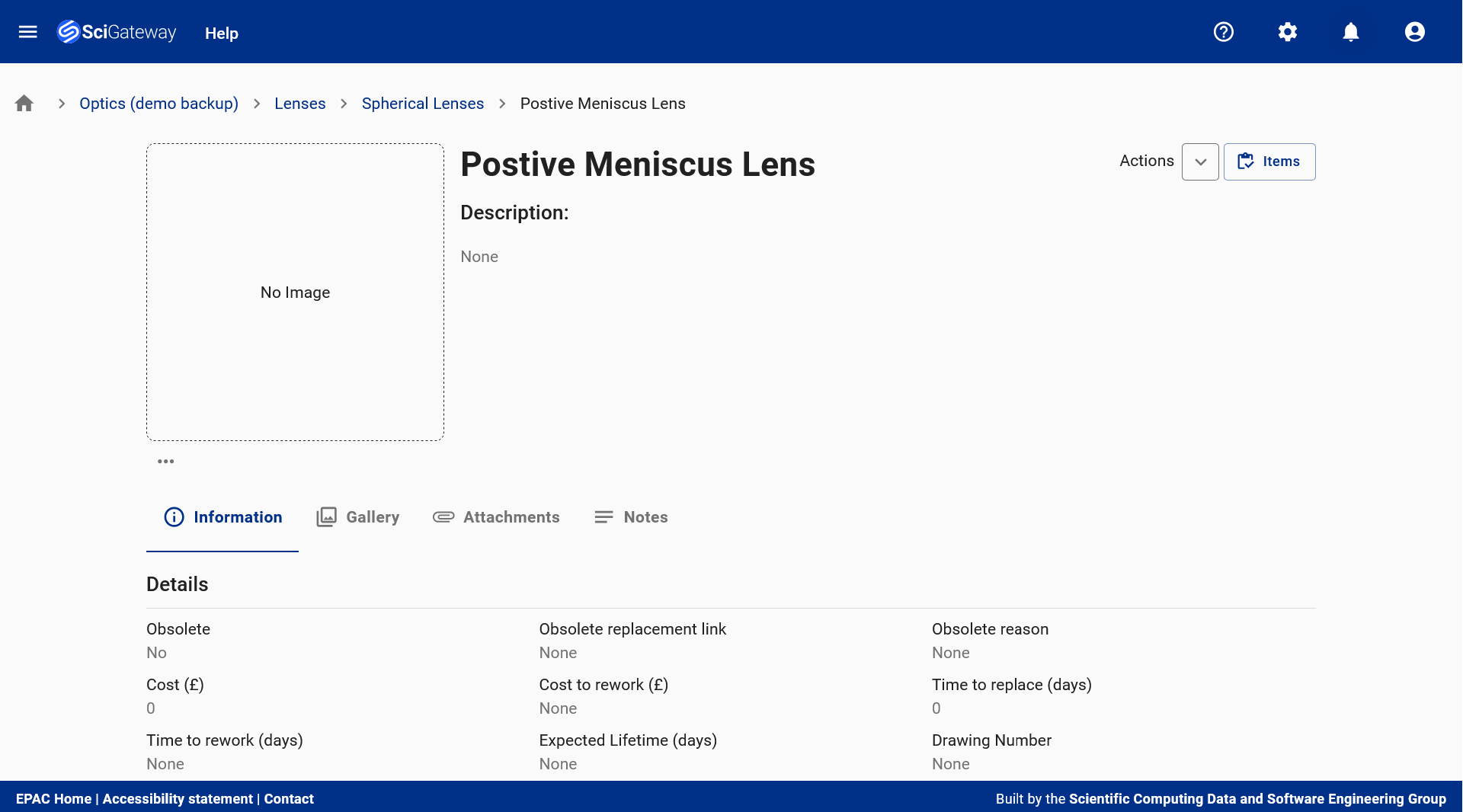 Catalogue Item Landing Page: Provides a centralised view of a catalogue item, combining technical specifications, metadata, gallery, attachments, and notes to support procurement, documentation, and lifecycle tracking.
Catalogue Item Landing Page: Provides a centralised view of a catalogue item, combining technical specifications, metadata, gallery, attachments, and notes to support procurement, documentation, and lifecycle tracking.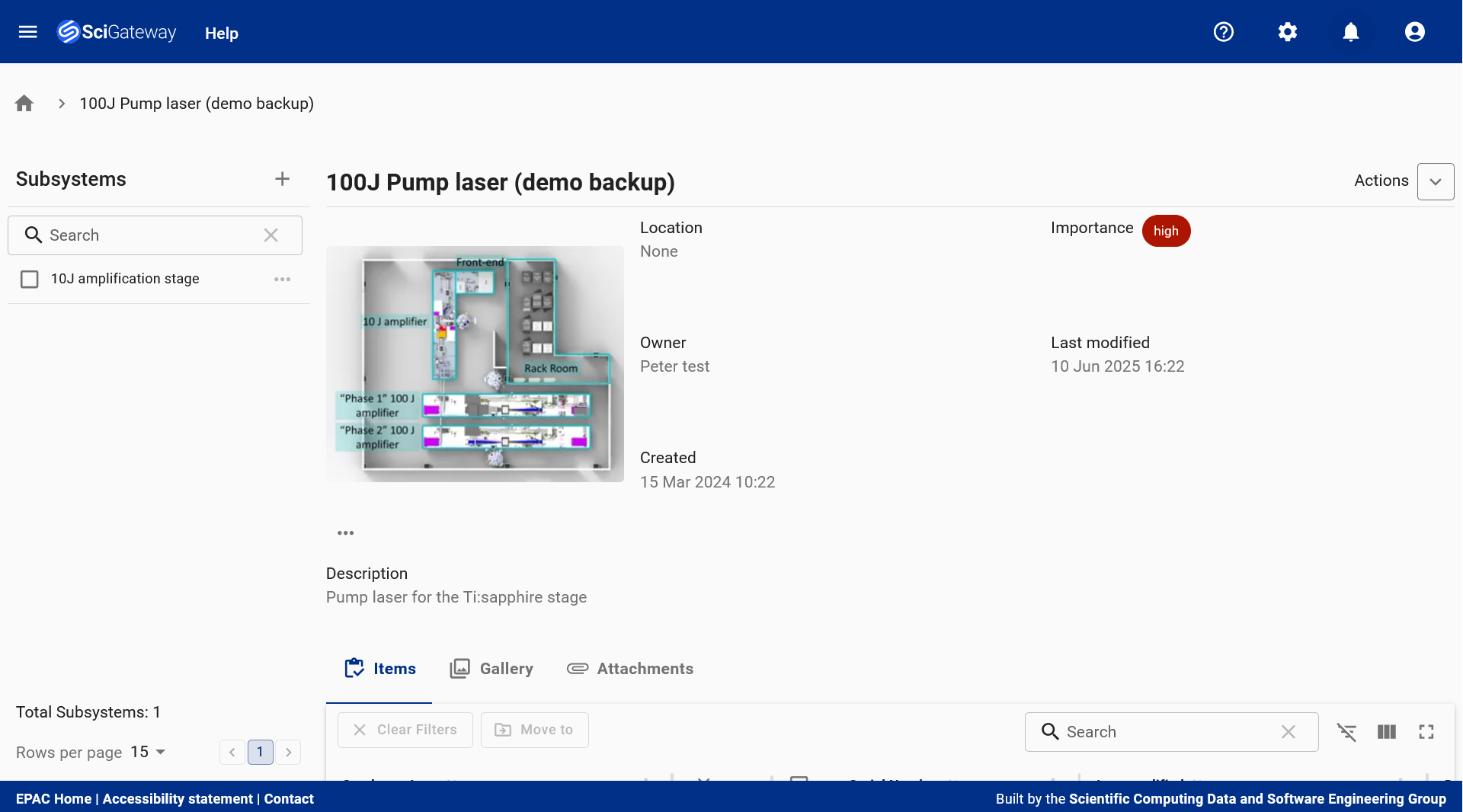 Subsystem Dashboard: Offers a comprehensive view of the '100J Pump Laser (Demo Backup)' subsystem, displaying its type, associated items, metadata, images, and attachments to support high-priority component tracking and lifecycle management.
Subsystem Dashboard: Offers a comprehensive view of the '100J Pump Laser (Demo Backup)' subsystem, displaying its type, associated items, metadata, images, and attachments to support high-priority component tracking and lifecycle management.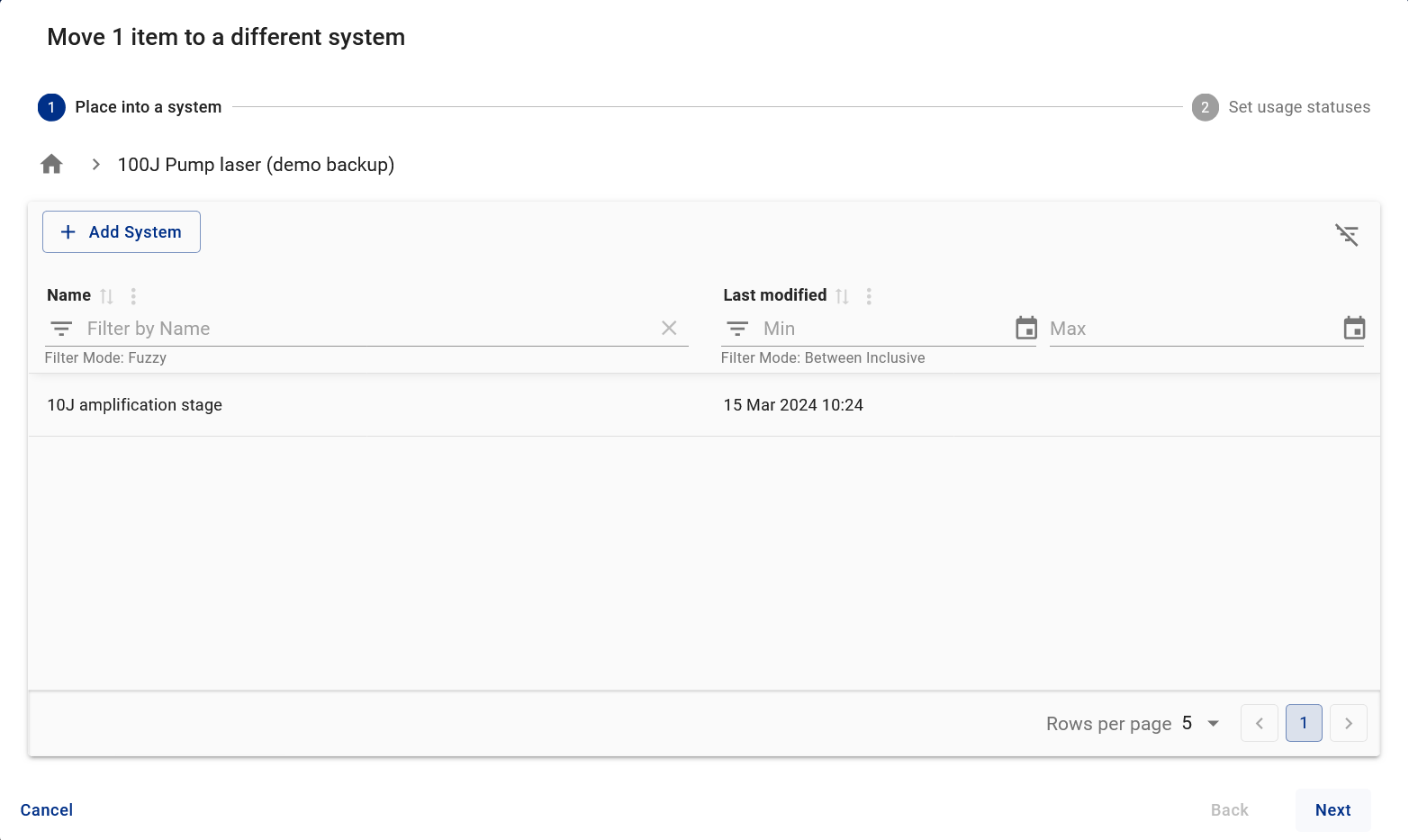 Moving Items: The 'Move To' Dialog facilitates the transfer of physical items from storage into the '100J Pump Laser (Demo Backup)' subsystem - ensuring accurate tracking and seamless integration within the system hierarchy. Movement of items between systems is restricted based on rules.
Moving Items: The 'Move To' Dialog facilitates the transfer of physical items from storage into the '100J Pump Laser (Demo Backup)' subsystem - ensuring accurate tracking and seamless integration within the system hierarchy. Movement of items between systems is restricted based on rules.Applications
How can IMS apply to you
Transportation & Logistics - Manage parts for vehicles, equipment, and infrastructure across depots and distribution hubs.
Manufacturing - Manage machine components, tooling, and maintenance-critical parts across production lines.
Healthcare - Manage parts for equipment used at healthcare facilities.
Research Facilities - Manage specialised parts for instruments, laboratories, and experimental infrastructure.
The Software
IMS is built using a modular microservice architecture:
IMS API – Manages core inventory entities such as items and catalogues.
Object Storage API – Handles file attachments and images.
LDAP JWT Auth – Provides secure access using token-based authentication.
The frontend is composed of micro frontends for flexibility and scalability:
IMS UI – User interface for interacting with inventory data.
SciGateway UI – Manages authentication and navigation across modules.
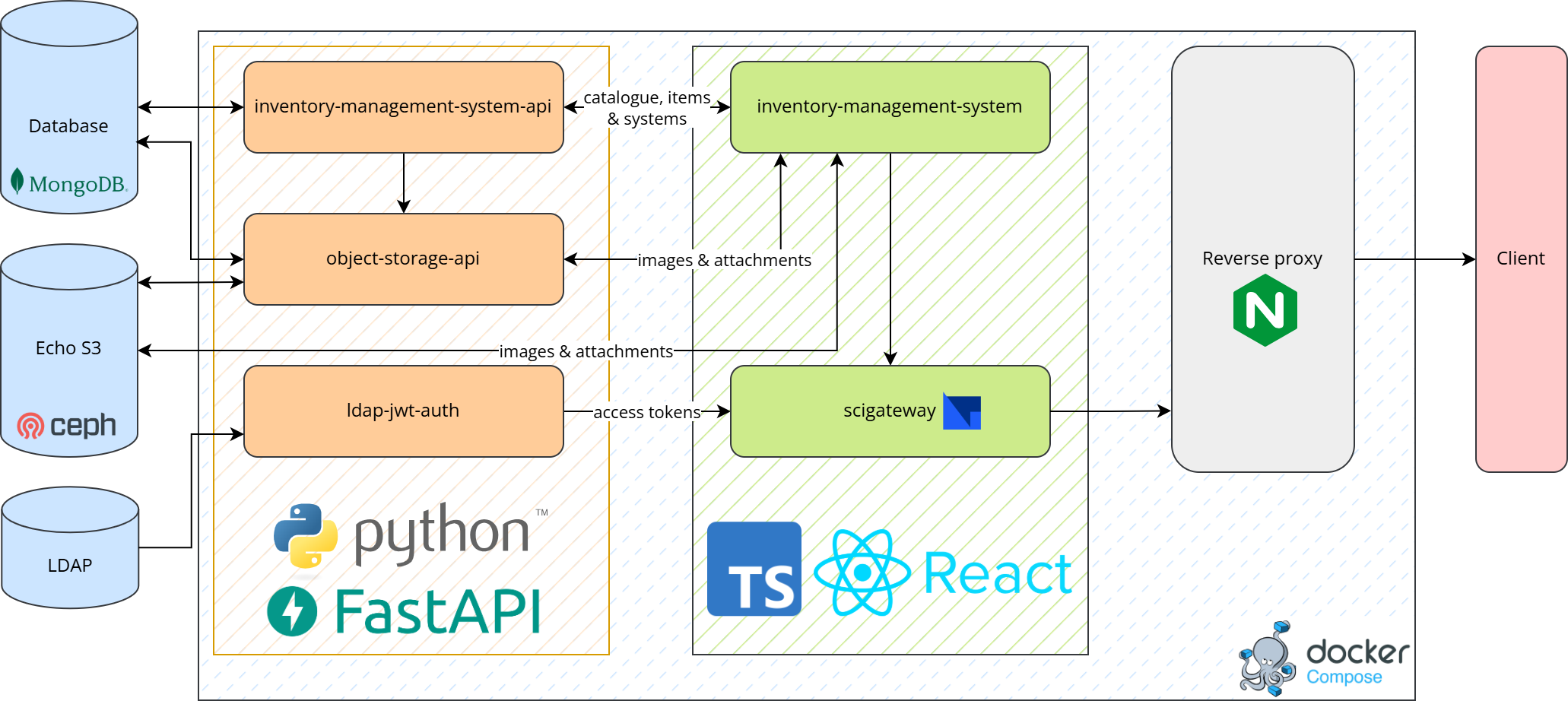 IMS Architecture Diagram
IMS Architecture DiagramContact Us
Please email the development team at ims-support@stfc365.onmicrosoft.com for any enquiries.
